Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Student's elbow; Olecranon bursitis; Housemaid's knee; Prepatellar bursitis; Weaver's bottom; Ischial gluteal bursitis; Baker's cyst; Gastrocnemius - semimembranosus bursa DefinitionBursitis is the swelling and irritation of a bursa. A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between muscles, tendons, and bones. CausesBursitis is often a result of overuse. It can also be caused by a change in activity level, such as training for a marathon, or by being overweight. Other causes include trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or infection. Sometimes, the cause can't be found. Bursitis commonly occurs in the shoulder, knee, elbow, and hip. Other areas that may be affected include the area around the Achilles tendon and the foot. SymptomsSymptoms of bursitis may include any of the following:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam. Tests that may be ordered include:
TreatmentYour provider will talk to you about a treatment plan to help you resume your normal activities, including some of the following tips. Tips to relieve bursitis pain:
For bursitis around the hips, knees, or ankle:
You should avoid activities that involve repetitive movements of any body part when possible. Other treatments include:
As the pain goes away, your provider may suggest exercises to build strength and keep mobility of movement in the painful area. In rare cases, surgery is done. Outlook (Prognosis)Most people do well with treatment. When the cause cannot be corrected, you may have long-term pain. Possible ComplicationsIf the bursa is infected, it becomes more inflamed and painful. This often requires antibiotics or surgery. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if symptoms recur or do not improve after 3 to 4 weeks of treatment, or if the pain is getting worse. PreventionWhen possible, avoid activities that include repetitive movements of any body parts. Be aware of your posture when doing the activities. Strengthening your muscles and working on your balance may help decrease the risk of bursitis. ReferencesBiundo JJ, Canoso JJ. Bursitis, tendinopathy, other periarticular disorders, and sports medicine. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 242. Hogrefe C, Jones EM. Tendinopathy and bursitis. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 103. | |
| |
Review Date: 8/27/2024 Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

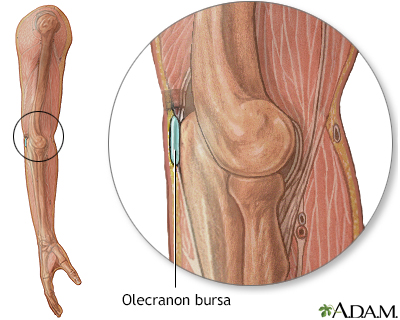 Bursa of the elbow
Bursa of the elbow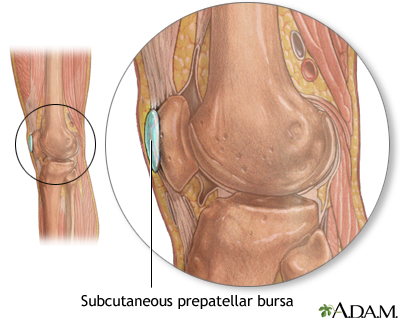 Bursa of the knee
Bursa of the knee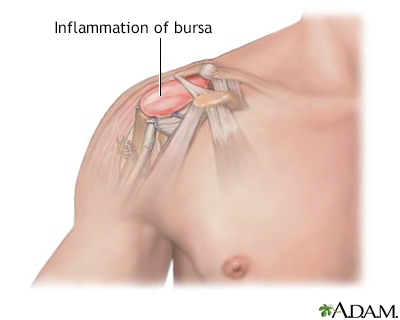 Bursitis of the sh...
Bursitis of the sh...
