Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Platelet storage pool disorder; Glanzmann's thrombasthenia; Bernard-Soulier syndrome; Platelet function defects - congenital DefinitionCongenital platelet function defects are conditions that prevent clotting elements in the blood, called platelets, from working as they should. Platelets help the blood clot. Congenital means present from birth. CausesCongenital platelet function defects are bleeding disorders that cause reduced platelet function. Most of the time, people with these disorders have a family history of a bleeding disorder, such as:
SymptomsSymptoms may include any of the following:
Exams and TestsThe following tests may be used to diagnose this condition:
You may need other tests. Your relatives may need to be tested. TreatmentThere is no specific treatment for these disorders. However, your health care provider will likely monitor your condition. You may also need:
Outlook (Prognosis)There is no cure for congenital platelet function disorders. Most of the time, treatment can control the bleeding. Possible ComplicationsComplications may include:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if:
PreventionA blood test can detect the gene responsible for the platelet defect. You may wish to seek genetic counseling if you have a family history of this problem and are considering having children. ReferencesHall JE, Hall ME. Hemostasis and blood coagulation. In: Hall JE, Hall ME, eds. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 37. Paola JD, O'Donnell JS. Von Willebrand disease and hemorrhagic abnormalities of platelet and vascular function. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 159. Rand ML, Israels SJ. Molecular basis of platelet function. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 124. | |
| |
Review Date: 2/3/2025 Reviewed By: Warren Brenner, MD, Oncologist, Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

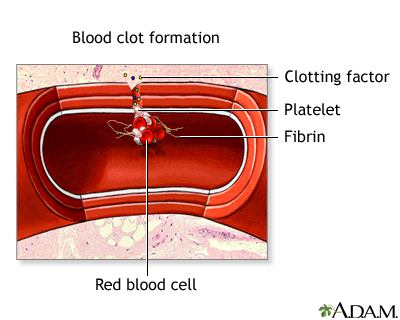 Blood clot formati...
Blood clot formati...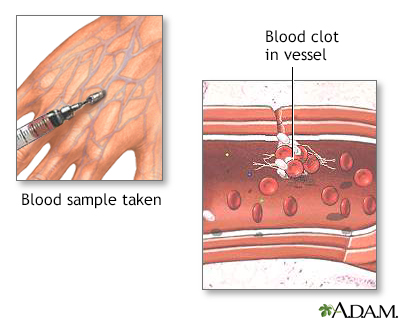 Blood clots
Blood clots
