Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Senile dementia - Alzheimer type (SDAT); SDAT; Dementia - Alzheimer; Alzheimer's disease DefinitionDementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. It affects memory, thinking, and behavior. Dementia may also be referred to as major neurocognitive disorder. CausesThe exact cause of Alzheimer disease is not known. Research shows that certain changes in the brain are associated with Alzheimer disease. This leads to structures called neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Most experts believe that this is the cause of Alzheimer disease but why this happens to some people is not known. You are more likely to develop Alzheimer disease if you:
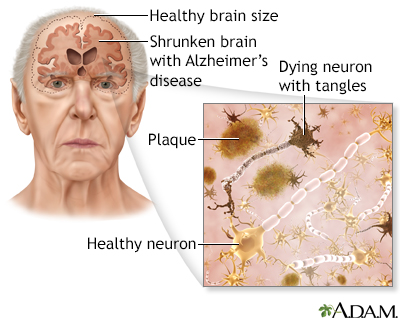 The following may also increase the risk:
There are two types of Alzheimer disease:
SymptomsAlzheimer disease symptoms include difficulty with many areas of mental function, including:
Alzheimer disease usually first appears as forgetfulness. Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a condition in which a person has more memory and thinking problems than other people their age. People with MCI have mild problems with thinking and memory that do not interfere with daily activities. They are often aware of the forgetfulness. Not everyone with MCI develops Alzheimer disease. Symptoms of MCI include:
Early symptoms of Alzheimer disease can include:
As Alzheimer disease becomes worse, symptoms are more obvious and interfere with the ability to take care of oneself. Symptoms may include:
People with severe Alzheimer disease can no longer:
Other symptoms that may occur with Alzheimer disease:
Exams and TestsA diagnosis of Alzheimer disease is made when certain symptoms are present, and by making sure other causes of dementia are not present. A skilled health care provider can often diagnose Alzheimer disease with the following steps:
Tests may be done to rule out other possible causes of dementia, including:
CT or MRI of the brain may be done to look for other causes of dementia, such as a brain tumor or stroke. The only way to know for certain that someone has Alzheimer disease is to examine a sample of their brain tissue after death. TreatmentThere is no cure for Alzheimer disease. The goals of treatment are:
Medicines are used to:
Before using these medicines, ask your provider:
Someone with Alzheimer disease will need support in the home as the disease gets worse. Family members or other caregivers can help by helping the person cope with memory loss and behavior and sleep problems. It is important to make sure the home of a person who has Alzheimer disease is safe for them. Support GroupsHaving Alzheimer disease or caring for a person with the condition may be a challenge. You can ease the stress of illness by seeking support through Alzheimer disease resources. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone. Outlook (Prognosis)How quickly Alzheimer disease gets worse is different for each person. If Alzheimer disease develops quickly, it is more likely to worsen quickly. People with Alzheimer disease often die earlier than normal, although a person may live anywhere from 3 to 20 years after diagnosis. Families will likely need to plan for their loved one's future care. The final phase of the disease may last from a few months to several years. During that time, the person becomes totally disabled. Death usually occurs from an infection or organ failure. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if:
PreventionAlthough there is no proven way to prevent Alzheimer disease, there are some measures that may help prevent or slow the onset of Alzheimer disease:
ReferencesAlzheimer's Association website. First practice guidelines for clinical evaluation of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias for primary and specialty care. [press release] July 22, 2018. aaic.alz.org/releases_2018/AAIC18-Sun-clinical-practice-guidelines.asp. Accessed May 8, 2024. Budson AE, Solomon PR. Alzheimer's disease. In: Budson AE, Solomon PR, eds. Memory Loss, Alzheimer's Disease, and Dementia. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 4. Knopman DS. Cognitive impairment and dementia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 371. Peterson RC, Graff-Radford J. Alzheimer disease and other dementias. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 95. Wilamowska K, Knoefel J. Alzheimer's disease. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2024. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2024:741-748. | |
| |
Review Date: 3/31/2024 Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Alzheimer disease
Alzheimer disease
