Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Skin infection - bacterial; Group A streptococcus - cellulitis; Staphylococcus - cellulitis DefinitionCellulitis is a common skin infection caused by bacteria. It affects the middle layer of the skin (dermis) and the tissues below. Sometimes, muscle below the skin can be affected. 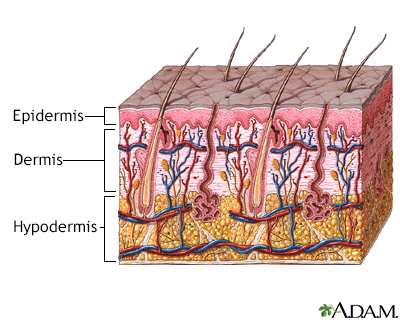 CausesStaphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria are the most common causes of cellulitis. Normal skin has many types of bacteria living on it. When there is a break in the skin, these bacteria can cause a skin infection. Risk factors for cellulitis include:
SymptomsSymptoms of cellulitis include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may reveal:
Your provider may mark the edges of the redness with a pen, to see if the redness goes past the marked border over the next several days. Tests that may be ordered include:
TreatmentYou will likely be prescribed antibiotics to take by mouth. You may be given pain medicine as well, if needed. At home, raise the infected area higher than your heart to reduce swelling and speed up healing. Rest until your symptoms improve. You may need to stay in a hospital if:
Outlook (Prognosis)Cellulitis usually goes away after taking antibiotics for 7 to 10 days. Longer treatment may be needed if cellulitis is more severe. This may occur if you have a chronic disease or your immune system is not working properly. People with fungal infections of the feet may have cellulitis that keeps coming back, especially if you have diabetes. Cracks in the skin from the fungal infection allow the bacteria to get into the skin. Possible ComplicationsThe following may result if cellulitis isn't treated or treatment doesn't work:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider right away if:
PreventionProtect your skin by:
Whenever you have a break in the skin:
ReferencesDinulos JGH. Bacterial infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9. James WD. Bacterial infections. In: James WD, ed. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 12. Pasternack MS, Swartz MN. Cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, and subcutaneous tissue infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 93. | |
| |
Review Date: 4/1/2025 Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Skin layers
Skin layers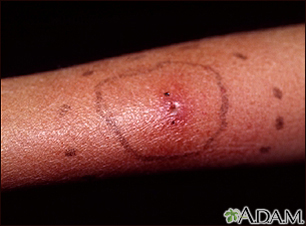 Cellulitis
Cellulitis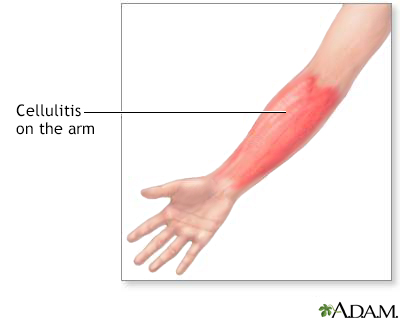 Cellulitis on the ...
Cellulitis on the ...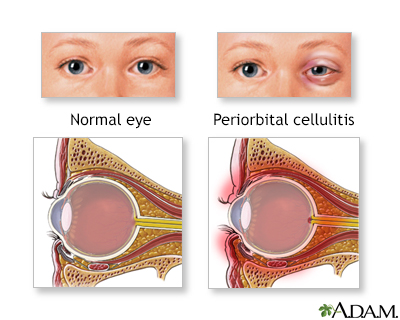 Periorbital cellul...
Periorbital cellul...
