Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Vomiting - dehydration; Diarrhea - dehydration; Diabetes - dehydration; Stomach flu - dehydration; Gastroenteritis - dehydration; Excessive sweating - dehydration DefinitionDehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much of your body's fluid is lost or not replaced. Severe dehydration is a life-threatening emergency. CausesYou can become dehydrated if you lose too much fluid, do not drink enough water or fluids, or both. Your body may lose a lot of fluid from:
You might not drink enough fluids because:
Older adults and people with certain diseases, such as diabetes, are also at higher risk for dehydration. SymptomsSigns of mild to moderate dehydration include:
Signs of severe dehydration include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will look for these signs of dehydration:
Your provider may do lab tests such as:
TreatmentTo treat dehydration:
For more severe dehydration or heat emergency, you may need to stay in a hospital and receive fluid through a vein (IV). The provider will also treat the cause of the dehydration. Dehydration caused by a stomach or intestinal virus should get better on its own after a few days. Outlook (Prognosis)If you notice signs of dehydration and treat it quickly, you should recover completely. Possible ComplicationsUntreated severe dehydration may cause:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalYou should call 911 or the local emergency number if:
PreventionTo prevent dehydration:
ReferencesKenefick RW, Cheuvront SN, Leon LR, O'Brien KK. Dehydration and rehydration. In: Auerbach PS, Cushing TA, Harris NS, eds. Auerbach's Wilderness Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 89. Padlipsky P, White W. Pediatric infectious diarrheal disease and dehydration. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 167. | |
| |
Review Date: 8/5/2023 Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

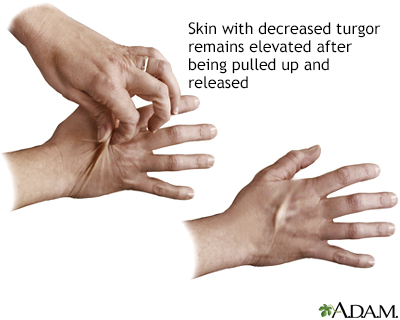 Skin turgor
Skin turgor
