Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Otospongiosis; Hearing loss - otosclerosis DefinitionOtosclerosis is an abnormal bone growth in the middle ear that causes hearing loss. CausesThe exact cause of otosclerosis is unknown. It may be passed down through families. People who have otosclerosis have an abnormal extension of sponge-like bone growing in the middle ear cavity. This growth prevents the ear bones from vibrating normally in response to sound waves. These vibrations are needed in order for you to hear. Otosclerosis is the most common cause of middle ear hearing loss in young adults. It typically begins in early to mid-adulthood. It is more common in women than in men. The condition may affect one or both ears. Risks for this condition include pregnancy and a family history of hearing loss. White people are more likely to develop this condition than people of other races. SymptomsSymptoms include:
Exams and TestsA hearing test (audiometry/audiology) may help determine the severity of hearing loss. A special imaging test of the head called a temporal-bone CT may be used to look for other causes of hearing loss. TreatmentOtosclerosis may slowly get worse. The condition may not need to be treated until you have more serious hearing problems. Using some medicines such as fluoride, calcium, or vitamin D may help to slow the hearing loss. However, the benefits of these treatments have not yet been proven. A hearing aid may be used to treat the hearing loss. This will not cure or prevent hearing loss from getting worse, but it may help with symptoms. Surgery can cure or improve conductive hearing loss. Either all or part of one of the small middle ear bones behind the eardrum (stapes) is removed and replaced with a prosthesis.
Outlook (Prognosis)Otosclerosis gets worse without treatment. Surgery can restore some or all of your hearing loss. Pain and dizziness from the surgery go away within a few weeks for most people. To reduce the risk of complications after surgery:
If surgery does not work, you may have total hearing loss. Treatment for total hearing loss involves developing skills to cope with deafness, and using hearing aids to transmit sounds from the non-hearing ear to the good ear. Possible ComplicationsComplications may include:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your health care provider if:
ReferencesHouse JW, Cunningham CD. Otosclerosis. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 146. Ironside JW, Smith C. Central and peripheral nervous systems. In: Cross SS, ed. Underwood Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 26. O'Handley JG, Tobin EJ, Shah AR. Otorhinolaryngology. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 18. Rivero A, Yoshikawa N. Otosclerosis. In: Myers EN, Snyderman CH, eds. Operative Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 133. | |
| |
Review Date: 5/2/2024 Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

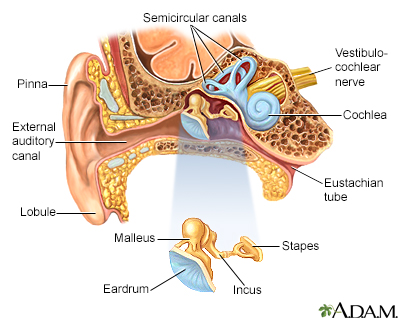 Ear anatomy
Ear anatomy
