Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Entero-enteral fistula; Enterocutaneous fistula; Fistula - gastrointestinal; Crohn disease - fistula DefinitionA gastrointestinal fistula is an abnormal opening in the stomach or intestines that allows the contents to leak to another part of the body.
CausesMost gastrointestinal fistulas occur after surgery. Other causes include:
SymptomsDepending on where the leak is, these fistulas may cause diarrhea, and poor absorption of nutrients. Your body may not have as much water and fluids as it needs.
Exams and TestsTests may include:
TreatmentTreatments may include:
Some fistulas close on their own after a few weeks to months. Outlook (Prognosis)The outlook depends on the person's overall health and how bad the fistula is. People who are otherwise healthy have a very good chance of recovery. Possible ComplicationsFistulas may result in malnutrition and dehydration, depending on their location in the intestine. They may also cause skin problems and infection. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your health care provider if you have:
ReferencesDe Prisco G, Celinski S, Spak CW. Abdominal abscesses and gastrointestinal fistulas. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 29. Nussbaum MS, McFadden DW. Gastric, duodenal, and small intestinal fistulas. In: Yeo CJ, ed. Shackleford's Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 76. | |
| |
Review Date: 6/11/2024 Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

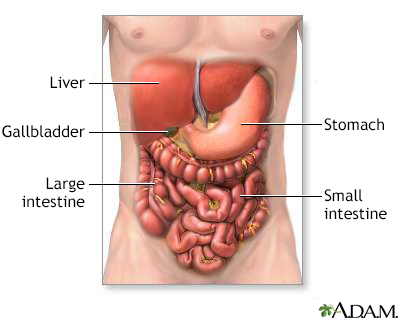 Digestive system o...
Digestive system o...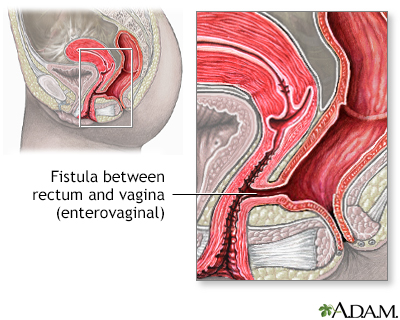 Fistula
Fistula
