Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
DefinitionGastritis occurs when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or swollen. Gastritis may last for only a short time (acute gastritis) or it may linger for months to years (chronic gastritis). CausesThe most common causes of gastritis are:
Less common causes are:
Trauma or a severe, sudden illness such as major surgery, kidney failure, or being placed on a breathing machine may cause gastritis. SymptomsMany people with gastritis do not have any symptoms. Symptoms you may notice are:
If gastritis is causing bleeding from the lining of the stomach, symptoms may include:
Exams and TestsTests that may be needed are:
TreatmentTreatment depends on what is causing the problem. Some of the causes will go away over time. You may need to stop taking aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, or other medicines that may be causing gastritis. Always talk to your health care provider before stopping any medicine. You may use other over-the-counter and prescription drugs that decrease the amount of acid in the stomach, such as:
Antibiotics may be used to treat gastritis caused by infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria. They are taken with an acid blocker such as a PPI or PCAB. Outlook (Prognosis)The outlook depends on the cause, but is often very good. Possible ComplicationsBlood loss and increased risk for gastric cancer can occur. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if you develop:
PreventionAvoid long-term use of substances that can irritate your stomach such as aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs, or alcohol. ReferencesFeldman M, Jensen PJ, Howden CW. Gastritis and gastropathy. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 52. Kuipers EJ. Acid peptic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 125. | |
| |
Review Date: 1/24/2025 Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Digestive system
Digestive system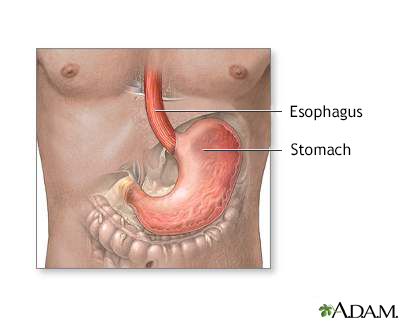 Stomach and stomac...
Stomach and stomac...
