Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
DefinitionThoracic outlet syndrome is a rare condition that involves:
The thoracic outlet is the area between the ribcage and collarbone. CausesNerves coming from the spine and major blood vessels of the body pass through a narrow space near your shoulder and collarbone on the way to the arms. Sometimes, there is not enough space for the nerves to pass by through the collarbone and upper ribs. Pressure (compression) on these blood vessels or nerves can cause symptoms in the arms or hands. Pressure may happen if you have:
People with this syndrome often have injured the area in the past or overused the shoulder. People with long necks and droopy shoulders may be more likely to develop this condition because of extra pressure on the nerves and blood vessels. SymptomsSymptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome may include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms. The following tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis:
Tests are also done to check for other problems, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or a damaged nerve due to problems in the neck. TreatmentPhysical therapy is often used to treat thoracic outlet syndrome. It aims to:
Your provider may prescribe pain medicine. If there is pressure on a vein, your provider may give you a blood thinner to prevent a blood clot. You may need surgery if physical therapy and changes in activity do not improve your symptoms. The surgeon may make a cut either under your armpit or just above your collarbone. During surgery, the following may be done:
Your surgeon may also suggest other alternatives, including angioplasty, if the artery is narrowed. Outlook (Prognosis)Surgery to remove the extra rib and break up tight fiber bands may ease symptoms in some people. Some people have symptoms that return after surgery. Possible ComplicationsComplications can occur with any surgery, and depend on the type of procedure and anesthesia. Risks related to this surgery include:
ReferencesFiller AG. Brachial plexus nerve entrapments and thoracic outlet syndromes. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 277. Grunebach H, Lum YW. Thoracic outlet syndrome: pathophysiology and diagnostic evaluation. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 123. | |
| |
Review Date: 10/9/2024 Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

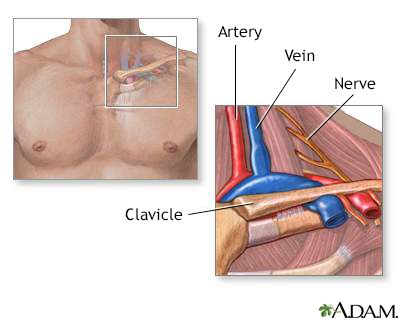 Thoracic outlet an...
Thoracic outlet an...
