Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Papular acrodermatitis of childhood; Infantile acrodermatitis; Acrodermatitis - infantile lichenoid; Acrodermatitis - papular infantile; Papulovesicular acro-located syndrome DefinitionGianotti-Crosti syndrome is a childhood skin condition that may be accompanied by mild symptoms of fever and malaise. It may also be associated with hepatitis B and other viral infections. CausesHealth care providers don't know the exact cause of this disorder. They do know that it is linked with other infections. In Italian children, Gianotti-Crosti syndrome is seen frequently with hepatitis B infection. But this link is rarely seen in the United States. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV, mononucleosis) is the virus most often associated with acrodermatitis. Other associated viruses include:
Bacterial infections such as Group A streptococcus and mycoplasma pneumoniae may also be associated with acrodermatitis. SymptomsSkin symptoms may include any of the following:
Other symptoms that may appear include:
Exams and TestsYour provider can diagnose this condition by looking at your skin and rash. Your liver, spleen, and lymph nodes may be swollen. The following tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions:
TreatmentThe disorder itself is not treated. Infections linked with this condition, such as hepatitis B and Epstein-Barr, are treated. Hydrocortisone creams and oral antihistamines may help with itching and irritation. Outlook (Prognosis)The rash usually disappears on its own in about 3 to 8 weeks without treatment or complication. Associated conditions must be watched carefully. Possible ComplicationsComplications occur as a result of associated conditions, rather than as a result of the rash. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if your child has signs of this condition. ReferencesDhossche JM, Chiu YE. Eczematous disorders. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 696. Mancini AJ, Shani-Adir J, Sidbury R. Other viral diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 81. | |
| |
Review Date: 4/1/2025 Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

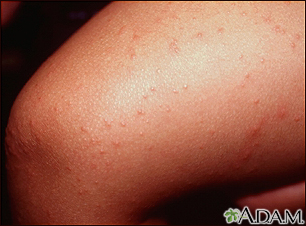 Gianotti-Crosti sy...
Gianotti-Crosti sy...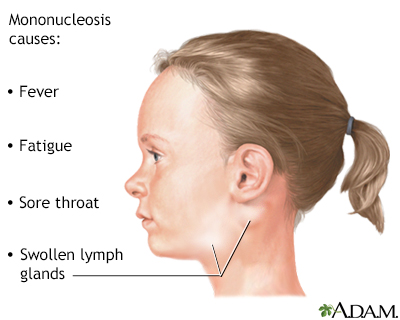 Infectious mononuc...
Infectious mononuc...
