Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Skin growths - fatty; Xanthelasma DefinitionXanthoma is a skin condition in which certain fats build up under the surface of the skin. CausesXanthomas are common, especially among older adults and people with high blood lipids (fats). Xanthomas vary in size. Some are very small. Others are bigger than 3 inches (in) or 7.5 centimeters (cm) in diameter. They may appear anywhere on the body. But, they are most often seen on the elbows, joints, tendons, knees, hands, feet, or buttocks. Xanthomas may be a sign of a medical condition that involves an increase in blood lipids (fats). Such conditions include:
Xanthelasma palpebra is a common type of xanthoma that appears on the eyelids. It usually occurs without any underlying medical condition. SymptomsSome xanthomas look like a yellow to orange bump (papule) with defined borders. There may be several individual ones or they may form clusters. Others, such as those next to tendons, do not affect the skin color. Exams and TestsYour health care provider will examine your skin. Usually, a diagnosis can be made by looking at xanthoma. If needed, your provider will remove a sample of the growth for testing (skin biopsy). You may have blood tests done to check lipid levels, liver function, and for diabetes. TreatmentIf you have a disease that causes increased blood lipids, treating the condition may help reduce the development of xanthomas. If the growth bothers you, your provider may remove it by surgery or with a laser. However, xanthomas may come back after surgery. Outlook (Prognosis)The growth is noncancerous and painless, but it may be a sign of another medical condition. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if xanthomas develop. They may indicate an underlying disorder that needs treatment. PreventionTo reduce the development of xanthomas, you may need to regulate your blood triglyceride and cholesterol levels. ReferencesDinulos JGH. Cutaneous manifestations of internal disease. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 26. James WD. Errors in metabolism. In: James WD, ed. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 21. Massengale WT. Xanthomas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 92. | |
| |
Review Date: 4/1/2025 Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

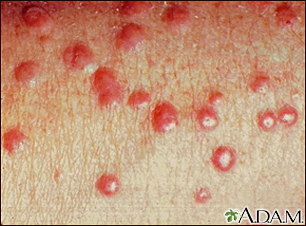 Xanthoma, eruptive...
Xanthoma, eruptive...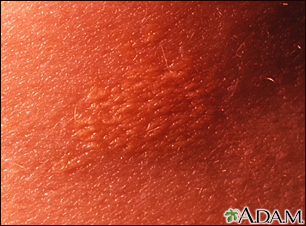 Xanthoma - close-u
Xanthoma - close-u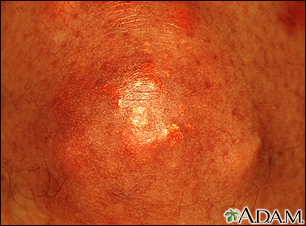 Xanthoma - close-u
Xanthoma - close-u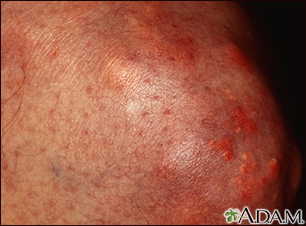 Xanthoma on the kn...
Xanthoma on the kn...
