Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
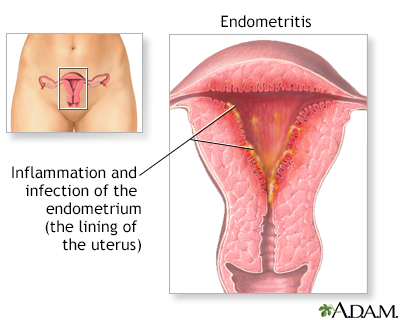
DefinitionEndometritis is an inflammation or irritation of the lining of the uterus (the endometrium). It is not the same as endometriosis. CausesEndometritis is caused by an infection in the uterus. It can be due to chlamydia, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, or a mix of normal vaginal bacteria. It is more likely to occur after miscarriage or childbirth. It is also more common after a long labor or C-section. The risk for endometritis is higher after having a pelvic procedure that is done through the cervix. Such procedures include:
Endometritis can occur at the same time as other pelvic infections. SymptomsSymptoms may include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will perform a physical exam with a pelvic exam. Your uterus and cervix may be tender and your provider may not hear bowel sounds. You may have cervical discharge. The following tests may be performed:
TreatmentYou will need to take antibiotics to treat the infection and prevent complications. Finish all your medicine if you have been given antibiotics after a pelvic procedure. Also, go to all recommended follow-up visits with your provider. You may need to be treated in the hospital if your symptoms are severe or occur after childbirth. Other treatments may involve:
Sexual partners may need to be treated if the condition is caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Outlook (Prognosis)In most cases, the condition goes away with antibiotics. Untreated endometritis can lead to more serious infections and complications. Rarely, it may be associated with a diagnosis of endometrial cancer. Possible ComplicationsComplications may include:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if you have symptoms of endometritis. Call right away if symptoms occur after:
PreventionEndometritis may be caused by STIs. To help prevent endometritis from STIs:
Women having a C-section may have antibiotics before the procedure to prevent infections. ReferencesCenters for Disease Control and Prevention website. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/default.htm. Updated June 13, 2023. Accessed September 27, 2023. Duff WP. Maternal and perinatal infection in pregnancy: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 58. Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23. | |
| |
Review Date: 7/12/2023 Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Endometritis
Endometritis
