Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Physiologic ovarian cysts; Functional ovarian cysts; Corpus luteum cysts; Follicular cysts DefinitionAn ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid that forms on or inside an ovary. This article is about cysts that form during your monthly menstrual cycle, called functional cysts. Functional cysts are not the same as cysts caused by cancer or other diseases. The formation of these cysts is a perfectly normal event and is a sign that the ovaries are working well. CausesEach month during your menstrual cycle, a follicle (cyst) grows on your ovary. The follicle is where an egg is developing.
Another type of cyst occurs after an egg has been released from a follicle. This is called a corpus luteum cyst. This type of cyst may contain a small amount of blood. This cyst makes progesterone and estrogen hormones. Ovarian cysts are more common in the childbearing years between puberty and menopause. The condition is less common after menopause. Taking fertility medicines often causes the development of multiple follicles (cysts) in the ovaries. These cysts most often go away after a woman's period, or after a pregnancy. Functional ovarian cysts are not the same as ovarian tumors or cysts due to hormone-related conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome. SymptomsOvarian cysts often cause no symptoms. An ovarian cyst is more likely to cause pain if it:
Symptoms of ovarian cysts can also include:
Changes in menstrual periods are not common with follicular cysts. These are more common with corpus luteum cysts. Spotting or bleeding may occur with some cysts. Exams and TestsYour health care provider may find a cyst during a pelvic exam, or when you have an ultrasound test for another reason. Ultrasound may be done to detect a cyst. Your provider may want to check you again in 6 to 8 weeks to make sure it is gone. Other imaging tests that may be done when needed include: The following blood tests may be done:
TreatmentFunctional ovarian cysts often do not need treatment. They often go away on their own within 8 to 12 weeks. If you have frequent ovarian cysts, your provider may prescribe birth control pills (oral contraceptives). These pills may reduce the risk of developing new cysts. Birth control pills do not decrease the size of current cysts. You may need surgery to remove the cyst or ovary to make sure that it is not ovarian cancer. Surgery is more likely to be needed for:
Types of surgery for ovarian cysts include: You may need other treatments if you have polycystic ovary syndrome or another disorder that can cause cysts. Outlook (Prognosis)Cysts in women who are still having periods are more likely to go away. A complex cyst in a woman who is past menopause has a higher risk of being cancer. Cancer is very unlikely with a simple cyst. Possible ComplicationsComplications have to do with the condition causing the cysts. Complications can occur with cysts that:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if:
Also contact your provider if you have had following on most days for at least 2 weeks:
These symptoms may indicate ovarian cancer. Studies which encourage women to seek care for possible ovarian cancer symptoms have not shown any benefit. Unfortunately, there is no proven effective means of screening for ovarian cancer. PreventionIf you are not trying to get pregnant and you often get functional cysts, you can prevent them by taking birth control pills. These pills prevent follicles from growing. ReferencesBrown DL, Wall DJ. Ultrasound evaluation of the ovaries. In: Norton ME, Scoutt LM, Feldstein VA, eds. Callen's Ultrasonography in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 30. Bulun SE, Babayev E. Physiology and pathology of the female reproductive axis. In Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 15. Dolan MS, Hill CC, Valea FA. Benign gynecologic lesions: vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, oviduct, ovary, ultrasound imaging of pelvic structures. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18. Kajal D, Levine D. The fetal urogenital tract. In: Rumack CM, Levine D, eds. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 40. | |
| |
Review Date: 3/31/2024 Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

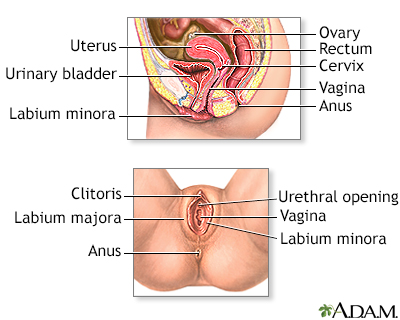 Female reproductiv...
Female reproductiv...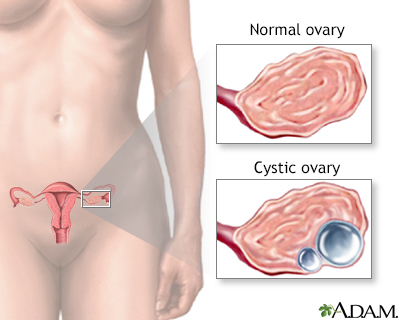 Ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts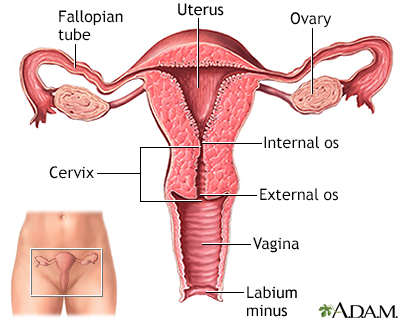 Uterus
Uterus
