Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Acrocephalosyndactyly DefinitionApert syndrome is a genetic disease in which the seams between the skull bones close earlier than normal. This affects the shape of the head and face. Children with Apert syndrome often have deformities of the hands and feet as well. CausesApert syndrome can be passed down through families (inherited) as an autosomal dominant trait. This means that only one parent needs to pass on the altered gene to a child to have the condition. Most cases may occur without a known family history. Apert syndrome is caused by one of two changes to the FGFR2 gene. This gene change causes some of the bony sutures of the skull to close too early. This condition is called craniosynostosis. SymptomsSymptoms include:
Several other syndromes can lead to a similar appearance of the face and head, but do not include the severe hand and foot features of Apert syndrome. These similar syndromes include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will perform a physical exam. Hand, foot, and skull x-rays will be done. Hearing tests should always be performed. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis of Apert syndrome. TreatmentTreatment consists of surgery to correct abnormal bone growth of the skull, as well as for the fusion of the fingers and toes. Children with this disorder should be examined by a specialized craniofacial surgery team at a children's medical center. A hearing specialist should be consulted if there are hearing problems. Support GroupsMore information and support for people with Apert syndrome and their families can be found at:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if you have a family history of Apert syndrome or you notice your baby's skull is not developing normally. PreventionGenetic counseling may be helpful if you have a family history of this disorder and are planning to become pregnant. Your provider can test your baby for this disease during pregnancy. ReferencesGoldstein JA, Davit AJ, Losee JE. Pediatric plastic surgery. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 23. Kinsman SL, Johnston MV. Congenital anomalies of the central nervous system. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 609. Mauck BM. Congenital anomalies of the hand. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 80. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center website. Acrocephalosyndactyly type I. rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/5833/apert-syndrome. Updated September 2025. Accessed October 15, 2025. | |
| |
Review Date: 9/18/2023 Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

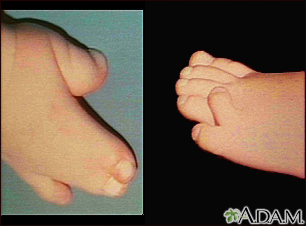 Syndactyly
Syndactyly
