Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
DefinitionNoonan syndrome is a disease present from birth (congenital) that causes many parts of the body to develop abnormally. In about 50% of cases, it is passed down through families (inherited). CausesNoonan syndrome is linked to variants in several genes. In general, certain proteins involved in growth and development become overactive as a result of these gene changes. Noonan syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition. This means only one parent has to pass down the variant gene for the child to have the syndrome. However, some cases may not be inherited and instead happen by chance (spontaneously). SymptomsSymptoms include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may show signs of heart problems the infant had from birth. These may include pulmonary stenosis and atrial septal defect. Tests depend on the symptoms, but may include:
Genetic testing can help diagnose this syndrome. TreatmentThere is no specific treatment. Your provider will suggest treatment to relieve or manage symptoms. Growth hormone has been used successfully to treat short height in some people with Noonan syndrome. Support GroupsMore information and support for people with Noonan syndrome and their families can be found at -- www.teamnoonan.org, and www.rasopathiesnet.org. Possible ComplicationsComplications may include:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalThis condition may be found during early infant exams. A geneticist is often needed to diagnose Noonan syndrome. PreventionCouples with a personal or family history of Noonan syndrome may want to consider genetic counseling before having children. ReferencesCooke DW, Divall SA, Radovick S. Normal and aberrant growth in children. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 25. Madan-Khetarpal S, Arnold G, Ortiz D. Genetic disorders and dysmorphic conditions. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 1. Mitchell AL. Congenital anomalies. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 29. | |
| |
Review Date: 3/31/2024 Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

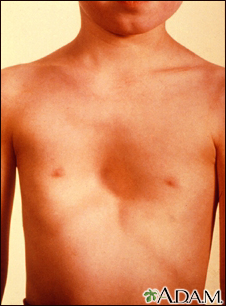 Pectus excavatum
Pectus excavatum
