Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome; HGPS DefinitionProgeria is a rare genetic condition that produces rapid aging in children. CausesProgeria is a rare condition. It is remarkable because its symptoms strongly resemble normal human aging, but it occurs in young children. In most cases, it is not passed down through families. It is rarely seen in more than one child in a family. SymptomsSymptoms include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will perform a physical exam and order laboratory tests. This may show:
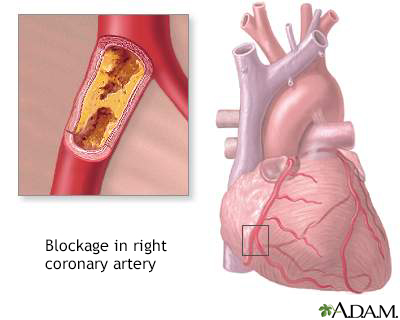
Cardiac stress testing may reveal signs of early atherosclerosis of blood vessels. Genetic testing can detect changes in the gene (LMNA) that causes progeria. TreatmentThere is no specific treatment for progeria. Aspirin and statin medicines may be used to protect against a heart attack or stroke. Support GroupsMore information and support for people with Progeria and their families can be found at:
Outlook (Prognosis)Progeria causes early death. People with the condition most often only live to their teenage years (average lifespan of 14 years). However, some can live into their early 20s. The cause of death is very often related to the heart or a stroke. Possible ComplicationsComplications may include:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if your child does not appear to be growing or developing normally. ReferencesGordon LB. Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (progeria). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 109. Jones KL, Jones MC, del Campo M. Senile-like appearance. In: Jones KL, Jones MC, del Campo M, eds. Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:174-197. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center website. Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7467/hutchinson-gilford-progeria-syndrome. Updated February 2023. Accessed October 17, 2023. | |
| |
Review Date: 9/18/2023 Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Coronary artery bl...
Coronary artery bl...
