Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Epiphora; Tearing - increased DefinitionWatery eyes means you have too many tears in and draining from the eyes. Tears help keep the surface of the eye moist. They wash away particles and foreign objects in the eye. CausesYour eyes always contain tears made by the tear (lacrimal) glands just above the eyes. These tears leave the eye through a small hole in the corner of the eye called the tear duct (nasolacrimal duct). Causes of watery eyes include:
Increased tearing sometimes happens with: One of the most common causes of excess tearing is dry eyes. Drying causes the eyes to become uncomfortable, which stimulates the body to produce too many tears. One of the main tests for diagnosing excess tearing is to check whether the eyes are too dry. Home CareThe treatment depends on the cause of the problem. Therefore, it is important to determine the cause before treating yourself at home. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalTearing is rarely an emergency. You should seek help right away if:
Also, contact your health care provider if you have:
What to Expect at Your Office VisitYour provider will examine your eyes and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms. Questions may include:
Your provider may order tests to help determine the cause. The treatment depends on the cause of the problem. ReferencesBorooah S, Tint NL. The visual system. In: Dover AR, Innes JA, Fairhurst K, eds. Macleod's Clinical Examination. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2024:chap 8. Olitsky SE, Marsh JD. Disorders of the lacrimal system. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 665. Örge FH, Salem ZM. Examination and common problems in the neonatal eye. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 99. Seller RH, Symons AB. Vision problems and other common eye problems. In: Seller RH, Symons AB, eds. Differential Diagnosis of Common Complaints. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 34. | |
| |
Review Date: 10/1/2025 Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Regional Medical Director of Penn Medicine Primary and Specialty Care, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

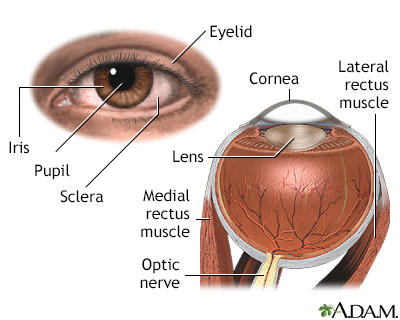 External and inter...
External and inter...
