Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Swallowing - pain or burning; Odynophagia; Burning feeling when swallowing, dysphagia DefinitionPainful swallowing is any pain or discomfort while swallowing. You may feel it high in the neck or lower down behind the breastbone. Most often, the pain feels like a strong sensation of squeezing or burning. Painful swallowing may be a symptom of a serious disorder. ConsiderationsSwallowing involves many nerves and muscles in the mouth, throat area, and food pipe (esophagus). Part of swallowing is voluntary. This means you are aware of controlling the action. However, much of swallowing is involuntary once it starts. Problems at any point in the swallowing process (including chewing, moving food to the back of the mouth, or moving it to the stomach) can result in painful swallowing. Swallowing problems can cause symptoms such as:
CausesSwallowing problems may be due to infections, such as:
Swallowing problems may be due to a problem with the esophagus, such as:
Other causes of swallowing problems include:
Home CareSome tips that may help you to ease swallowing pain at home include:
If someone is choking, immediately perform the Heimlich maneuver. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your health care provider if you have painful swallowing and:
Tell your provider about any other symptoms that occur with the painful swallowing, including:
What to Expect at Your Office VisitYour provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms, including:
The following tests may be done:
ReferencesAllen CT, Nussenbaum B, Merati AL. Acute and chronic laryngopharyngitis. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 61. DeVault KR. Symptoms of esophageal disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 13. Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. Esophageal neuromuscular function and motility disorders. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 44. Wilcox CM. Gastrointestinal consequences of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 35. | |
| |
Review Date: 8/7/2023 Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

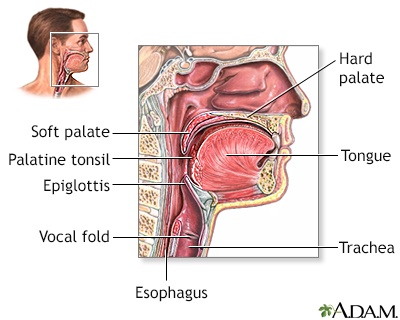 Throat anatomy
Throat anatomy
