Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Pain - shoulder DefinitionShoulder pain is any pain in or around the shoulder joint. ConsiderationsThe shoulder is the most movable joint in the human body. A group of four muscles and their tendons, called the rotator cuff, give the shoulder its wide range of motion. 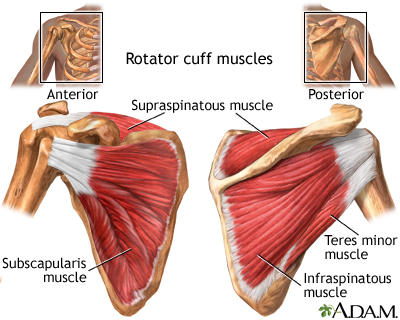 Swelling, damage, or bone changes around the rotator cuff can cause shoulder pain. You may have pain when lifting the arm above your head or moving it forward or behind your back. CausesThe most common cause of shoulder pain occurs when rotator cuff tendons become trapped under the bony area in the shoulder. The tendons become inflamed or damaged. This condition is called rotator cuff tendinitis or bursitis. 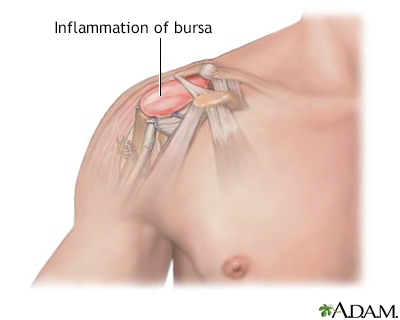 Shoulder pain may also be caused by:
Sometimes, shoulder pain may be due to a problem in another area of the body, such as the neck or lungs. This is called referred pain. There is usually pain at rest and no worsening of pain when moving the shoulder. Home CareHere are some tips for helping shoulder pain get better:
Rotator cuff problems can be treated at home also.
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalSudden left shoulder pain can sometimes be a sign of a heart attack. Call 911 or the local emergency number if you have sudden pressure or crushing pain in your shoulder, especially if the pain runs from your chest to the left jaw, arm or neck, or occurs with shortness of breath, dizziness, or sweating. 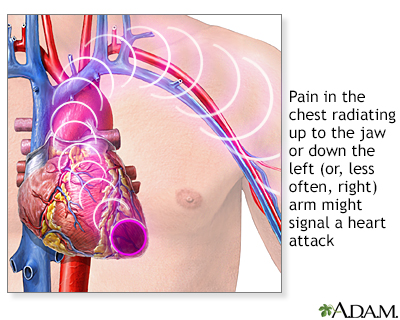 Go to the hospital emergency room if you have just had a severe injury and your shoulder is very painful, swollen, bruised, or bleeding. Contact your provider if you have:
What to Expect at Your Office VisitYour provider will perform a physical exam and closely look at your shoulder. You will be asked questions to help the provider understand your shoulder problem. Blood or imaging tests, such as x-rays, ultrasound, or MRI, may be ordered to help diagnose the problem. Your provider may recommend treatment for shoulder pain, including:
If you have a rotator cuff problem, your provider will likely suggest self-care measures and exercises. ReferencesGill TJ. Shoulder diagnosis and decision-making. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: Principles and Practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 37. Martin SD, Thornhill TS. Shoulder pain. In: Firestein GS, McInnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 46. | |
| |
Review Date: 9/2/2025 Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

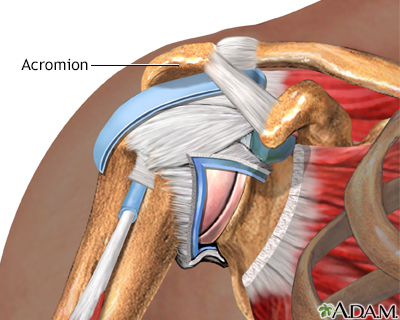 Impingement syndro...
Impingement syndro... Rotator cuff muscl...
Rotator cuff muscl... Heart attack sympt...
Heart attack sympt... Bursitis of the sh...
Bursitis of the sh...
