Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Extra digits; Supernumerary digits DefinitionPolydactyly is a condition in which a person has more than 5 fingers per hand or 5 toes per foot. ConsiderationsHaving extra fingers or toes (6 or more) can occur on its own. There may not be any other symptoms or disease present. Polydactyly may be passed down in families. This trait involves only one gene that can cause several variations. African Americans, more than other ethnic groups, can inherit a 6th finger. In most cases, this is not caused by a genetic disease. Polydactyly can also occur with some genetic diseases. Extra digits may be poorly developed and attached by a small stalk. This most often occurs on the little finger side of the hand. Poorly formed digits are usually removed. Simply tying a tight string around the stalk can cause it to fall off in time if there are no bones in the digit. In some cases, the extra digits may be well-formed and can even function. Larger digits may need surgery to be removed. CausesCauses may include:
Home CareYou may need to take steps at home after surgery to remove an extra digit. These steps may include checking the area to make sure the area is healing and changing the dressing. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalMost of the time, this condition is discovered at birth when the baby is still in the hospital. What to Expect at Your Office VisitThe health care provider will diagnose the condition based on a family history, medical history, and a physical exam. Medical history questions may include:
Tests used to diagnose the condition:
You may want to make a note of this condition in your personal medical record. Extra digits may be discovered after the first 3 months of pregnancy with ultrasound or a more advanced test called embryofetoscopy. ReferencesCarrigan RB. The upper limb. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 722. Mauck BM. Congenital anomalies of the hand. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 80. Son-Hing JP, Hardesty CK. Congenital abnormalities of the upper and lower extremities and spine. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 103. | |
| |
Review Date: 10/1/2025 Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Regional Medical Director of Penn Medicine Primary and Specialty Care, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

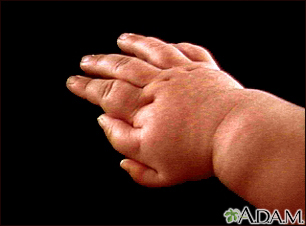 Polydactyly - an i...
Polydactyly - an i...
