Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Pilonidal abscess; Pilonidal sinus; Pilonidal cyst; Pilonidal disease DefinitionPilonidal sinus disease is an inflammatory condition involving the hair follicles that can occur anywhere along the crease between the buttocks, which runs from the bone at the bottom of the spine (sacrum) to the anus. The disease is benign and has no association with cancer. Pilonidal disease may appear as:
ConsiderationsSymptoms may include:
There may be no symptoms other than a small dent (pit) in the skin in the crease between the buttocks. CausesThe cause of pilonidal disease is not clear. It is thought to be caused by hair growing into the skin in the crease between the buttocks. This problem is more likely to occur in people who:
Home CareWash normally and pat dry. Use a soft bristle scrub brush to prevent the hairs from becoming ingrown. Keep the hairs in this region short (shaving, laser, depilatory) which may decrease the risk of flare-ups and recurrence. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your health care provider if you notice any of the following around a pilonidal cyst:
What to Expect at Your Office VisitYou will be asked for your medical history and given a physical examination. Sometimes you may be asked for the following information:
Pilonidal disease that causes no symptoms does not need to be treated. A pilonidal abscess may be opened, drained, and packed with gauze. Antibiotics may be used if there is an infection spreading in the skin or you also have another, more severe illness. Other surgeries that may be needed include:
ReferencesGunter RL, Johnson EK, Steele SR. Anorectal: management of pilonidal disease. In: Cameron J, ed. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:287-350. Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al. Surgical conditions of the anus and rectum. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 392. Surrell JA. Pilonidal cyst and abscess: current management. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 31. | |
| |
Review Date: 11/25/2023 Reviewed By: Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, General Surgery Practice Specializing in Breast Cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

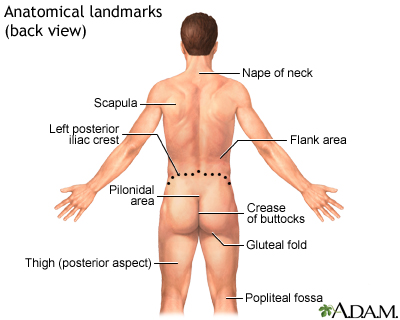 Anatomical landmar...
Anatomical landmar...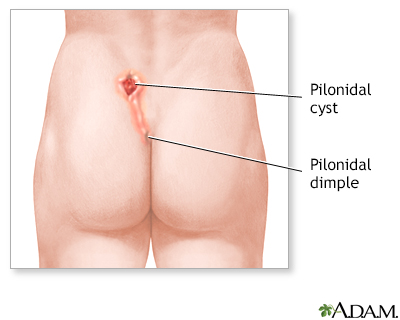 Pilonidal dimple
Pilonidal dimple
