Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Mass in the abdomen DefinitionAn abdominal mass is swelling in one part of the belly area (abdomen). ConsiderationsAn abdominal mass is often found during a routine physical exam. Most of the time, the mass develops slowly. You may not be able to feel the mass. Locating the mass helps your health care provider make a diagnosis. For example, the abdomen can be divided into four areas:
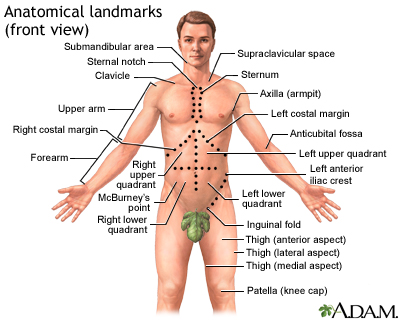 Other terms used to describe the location of abdominal pain or masses include:
The location of the mass and its firmness, texture, and other qualities can provide clues to its cause. CausesSeveral conditions can cause an abdominal mass:
Home CareAll abdominal masses should be examined as soon as possible by the provider. Changing your body position may help relieve pain due to an abdominal mass. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalGet medical help right away if you have a pulsating lump in your abdomen along with severe abdominal pain. This could be a sign of a ruptured aortic aneurysm, which is an emergency condition. Contact your provider if you notice any type of abdominal mass. What to Expect at Your Office VisitIn nonemergency situations, your provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your symptoms and medical history. In an emergency situation, you will be stabilized first. Then, your provider will examine your abdomen and ask questions about your symptoms and medical history, such as:
A pelvic or rectal exam may be needed in some cases. Tests that may be done to find the cause of an abdominal mass include:
ReferencesBall JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Abdomen. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 18. Landmann A, Bonds M, Postier R. Acute abdomen. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46. McQuaid KR. Approach to the patient with gastrointestinal disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 118. | |
| |
Review Date: 10/9/2024 Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Anatomical landmar...
Anatomical landmar...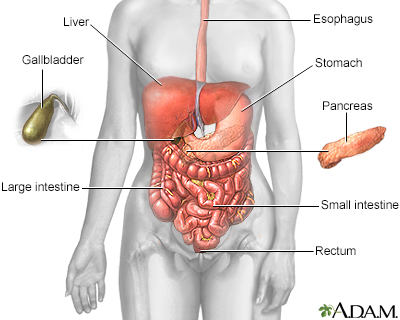 Digestive system
Digestive system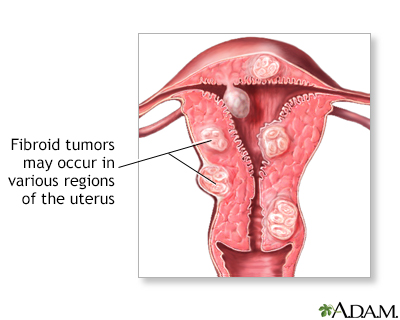 Fibroid tumors
Fibroid tumors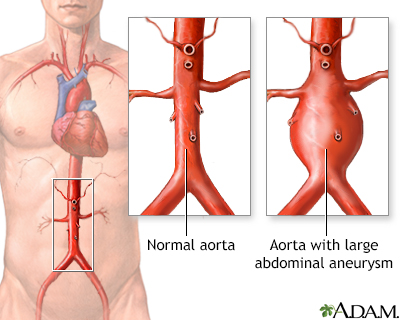 Aortic aneurysm
Aortic aneurysm
