Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Mongolian slant DefinitionThe palpebral slant is the direction of the slant of a line that goes from the outer corner of the eye to the inner corner. ConsiderationsThe word palpebral refers to the upper and lower eyelids, which help determine the shape of the eye. A line drawn from the inner corner to the outer corner determines the slant of the eye, or palpebral slant. Slanting and a fold of skin (epicanthal fold) are normal in people of Asian descent. Abnormal slanting of the eye may occur with some genetic disorders and syndromes. The most common of these is Down syndrome. People with Down syndrome often also have an epicanthal fold in the inner corner of the eye. CausesPalpebral slant may not be due to any defect. However, in some cases, it may be due to:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your health care provider if:
What to Expect at Your Office VisitYour provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your child's medical history and symptoms. An infant with an abnormal palpebral slant that is due to a problem will usually have other symptoms of another health condition. That condition will be diagnosed based on a family history, medical history, and a physical exam. Tests to confirm a disorder may include:
ReferencesKataguiri P, Kenyon KR. Corneal and external eye manifestations of systemic disease. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 4.25. Madan-Khetarpal S, Arnold G, Ortiz D. Genetic disorders and dysmorphic conditions. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 1. Orge FH, Salem ZM. Examination and common problems in the neonatal eye. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 99. Slavotinek AM. Dysmorphology, phenotyping, and sequences. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 100. | |
| |
Review Date: 4/5/2025 Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

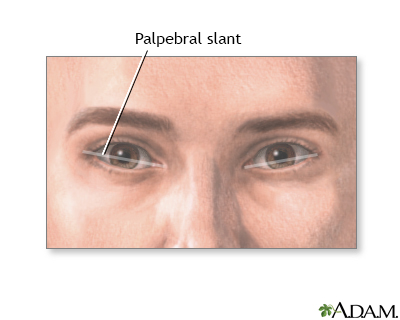 Palpebral slant
Palpebral slant
