Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Quantitative stool fat determination; Fat absorption DefinitionThe fecal fat test measures the amount of fat in the stool. This can help gauge the percentage of dietary fat that the body does not absorb. How the Test is PerformedThere are many ways to collect the samples.
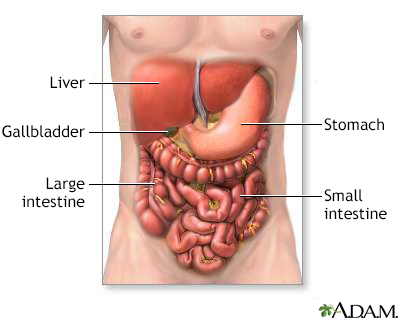
Collect all stool that is released over a 24-hour period (or sometimes 3 days) in the containers provided. Label the containers with name, time, and date, and send them to the lab. Sometimes you will be asked to provide a single stool sample to be examined under a microscope for stool fat. How to Prepare for the TestEat a normal diet containing about 100 grams (g) of fat per day for 3 days before starting the test. The health care provider may ask you to stop using medicines or food additives that could affect the test. How the Test will FeelThe test involves only normal bowel movements. There is no discomfort. Why the Test is PerformedThis test evaluates fat absorption to tell how well the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and intestines are working. Fat malabsorption can cause a change in your stools called steatorrhea. To absorb fat normally, the body needs bile from the gallbladder (or the liver if the gallbladder has been removed), enzymes from the pancreas, and a normal small intestine. Normal ResultsLess than 7 g of fat per 24 hours. What Abnormal Results MeanDecreased fat absorption may be caused by:
RisksThere are no risks. ConsiderationsFactors that interfere with the test are:
ReferencesHöegenauer C, Hammer HF. Maldigestion and malabsorption. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 104. Semrad CE. Approach to the patient with diarrhea and malabsorption. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 126. | |
| |
Review Date: 8/12/2024 Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Digestive system o...
Digestive system o...
