Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Luteinizing hormone response to gonadotropin-releasing hormone DefinitionLH response to GnRH is a blood test to help determine if your pituitary gland can correctly respond to gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH). LH stands for luteinizing hormone. How the Test is PerformedA blood sample is taken, and then you are given a shot of GnRH. After a specified time, more blood samples are taken so that LH can be measured. How to Prepare for the TestNo special preparation is necessary. How the Test will FeelWhen the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away. Why the Test is PerformedGnRH is a hormone made by the hypothalamus gland. LH is made by the pituitary gland. GnRH causes (stimulates) the pituitary gland to release LH. This test is used to tell the difference between primary and secondary hypogonadism. Hypogonadism is a condition in which the sex glands make little or no hormones. In men, the sex glands (gonads) are the testes. In women, the sex glands are the ovaries. Depending on the type of hypogonadism:
This test may also be done to check for the reason why there is a:
Normal ResultsNormal value ranges may vary slightly among different labs. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results. What Abnormal Results MeanAn increased LH response suggests a problem in the ovaries or testes. A reduced LH response suggests a problem with the hypothalamus gland or pituitary gland. Abnormal results may also be due to:
RisksThere is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others. Other risks related to having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
ReferencesCatherino WH. Reproductive endocrinology and infertility. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 218. Guber HA, Oprea M, Russell YX. Evaluation of endocrine function. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 25. Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 26. Kaiser U, Ho KKY. Pituitary physiology and diagnostic evaluation. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 6. | |
| |
Review Date: 8/18/2025 Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

 Blood test
Blood test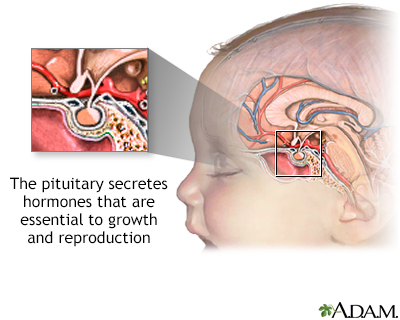 The pituitary glan
The pituitary glan
