Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Abdominal film; X-ray - abdomen; Flat plate; KUB x-ray DefinitionAn abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. The bones of the lower spine are also visible. When the test is done to look at the bladder and kidney structures, it is called a KUB (kidneys, ureters, bladder) x-ray. How the Test is PerformedThe test may be done in a hospital radiology department. Or, it may be done in the health care provider's office by an x-ray technologist. You lie on your back on the x-ray table. The x-ray machine is positioned over your abdominal area. You hold your breath as the picture is taken so that the picture will not be blurry. You may be asked to change position to the side or to stand up for additional pictures. Body parts not being imaged may be covered with a lead apron or shield to limit exposure to the x-rays. How to Prepare for the TestBefore having the x-ray, tell your provider the following:
You will wear a hospital gown during the x-ray procedure. You must remove all jewelry. How the Test will FeelThere is no discomfort. The x-rays are taken as you lie on your back, side, and while standing. Why the Test is PerformedYour provider may order this test to:
Normal ResultsThe x-ray will show normal structures for a person your age. What Abnormal Results MeanAbnormal findings include:
RisksThere is low radiation exposure. X-rays are monitored and regulated to provide the minimum amount of radiation exposure needed to produce the image. Most experts feel that the risk is low compared to the benefits. Pregnant women and children are more sensitive to the risks of the x-ray. Women should tell their provider if they are, or may be, pregnant. ReferencesAl Sarraf AA, McLaughlub PD, Maher MM. Current status of imaging of the gastrointestinal tract. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18. Rischall ML, Puskarich MA. Abdominal trauma. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 38. Tomei E, Cantisani V, Marcantonio A, D'Ambrosio U, Hayano K. Plain radiography of the abdomen. In: Sahani DV, Samir AE, eds. Abdominal Imaging. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 1. | |
| |
Review Date: 1/1/2025 Reviewed By: Jason Levy, MD, FSIR, Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

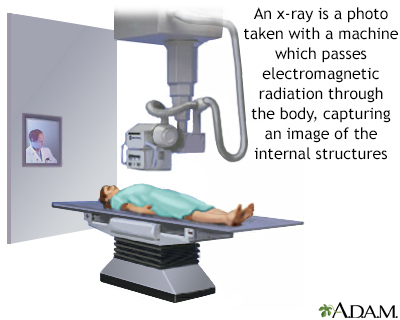 X-ray
X-ray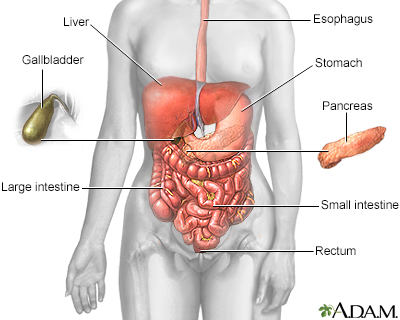 Digestive system
Digestive system
