Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Culture - amniotic fluid; Culture - amniotic cells; Alpha-fetoprotein - amniocentesis DefinitionAmniocentesis is a test that can be done during pregnancy to look for certain problems in the developing baby. These problems include:
How the Test is PerformedAmniocentesis removes a small amount of fluid from the sac around the baby in the womb (uterus). It is most often done in a health care provider's office or medical center. You do not need to stay in the hospital. You will have a pregnancy ultrasound first. This helps your provider see where the baby is in your womb. Numbing medicine is then rubbed onto part of your belly. Sometimes, the medicine is given through a shot in the skin on the belly area. The skin is cleaned with a disinfecting liquid. Your provider inserts a long, thin needle through your belly and into your womb. A small amount of fluid (about 4 teaspoons or 20 milliliters) is removed from the sac surrounding the baby. In most cases, the baby is watched by ultrasound during the procedure. The fluid is sent to a laboratory. Testing may include:
Results of genetic testing usually take about 2 weeks. Other test results come back in 1 to 3 days. Sometimes amniocentesis is also used later in pregnancy to:
How to Prepare for the TestYour bladder may need to be full for the ultrasound. Check with your provider about this. Before the test, blood may be taken to find out your blood type and Rh factor. You may get a shot of medicine called Rho(D) Immune Globulin (RhoGAM and other brands) if you are Rh negative. Why the Test is PerformedAmniocentesis is usually offered to women who are at increased risk of having a child with birth defects. This includes women who:
Genetic counseling is recommended before the procedure. This will allow you to:
This test:
Amniocentesis can be used to diagnose many different gene and chromosome problems in the baby, including:
Normal ResultsA normal result means:
Note: Amniocentesis typically is the most accurate test for genetic conditions and malformation, although rare, a baby may still have genetic or other types of birth defects, even if amniocentesis results are normal. What Abnormal Results MeanAn abnormal result may mean your baby has:
Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results. Ask your provider:
RisksRisks are minimal, but may include:
ReferencesDugoff L, Wapner RJ. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital disorders. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 30. Patterson DA, Andazola JJ. Amniocentesis. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 144. Russo ML, Mahoney R, Driscoll DA, Al-Kouatly H. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 12. | |
| |
Review Date: 8/18/2025 Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | |

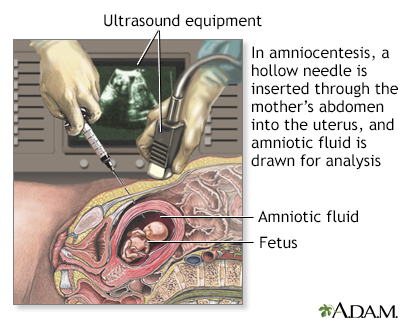 Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis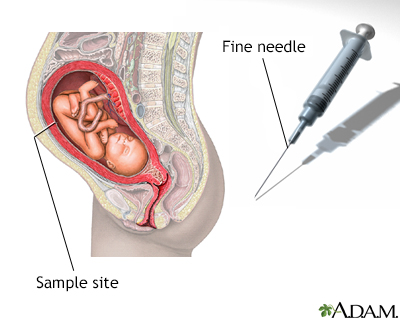 Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis
